Chapter 14 Appendix
14.1 Preface
14.1.1 Formatting
The following ggplot2 theme was use to format plots in this book:
plot_style <- function() {
font <- "Helvetica"
ggplot2::theme_classic() +
ggplot2::theme(
plot.title = ggplot2::element_text(
family = font, size=14, color = "#222222"),
plot.subtitle = ggplot2::element_text(
family=font, size=12, color = "#666666"),
legend.position = "right",
legend.background = ggplot2::element_blank(),
legend.title = ggplot2::element_blank(),
legend.key = ggplot2::element_blank(),
legend.text = ggplot2::element_text(
family=font, size=14, color="#222222"),
axis.title.y = ggplot2::element_text(
margin = ggplot2::margin(t = 0, r = 8, b = 0, l = 0),
size = 14, color="#666666"),
axis.title.x = ggplot2::element_text(
margin = ggplot2::margin(t = -2, r = 0, b = 0, l = 0),
size = 14, color = "#666666"),
axis.text = ggplot2::element_text(
family=font, size=14, color="#222222"),
axis.text.x = ggplot2::element_text(
margin = ggplot2::margin(5, b = 10)),
axis.ticks = ggplot2::element_blank(),
axis.line = ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor = ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.y = ggplot2::element_line(color = "#eeeeee"),
panel.grid.major.x = ggplot2::element_line(color = "#ebebeb"),
panel.background = ggplot2::element_blank(),
strip.background = ggplot2::element_rect(fill = "white"),
strip.text = ggplot2::element_text(size = 20, hjust = 0)
)
}Which you can then active with:
14.2 Introduction
14.2.1 Worlds Store Capacity
The following script was used to generate the worlds store capacity diagram:
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
read.csv("data/01-worlds-capacity-to-store-information.csv", skip = 8) %>%
gather(key = storage, value = capacity, analog, digital) %>%
mutate(year = X, terabytes = capacity / 1e+12) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = year, y = terabytes, group = storage)) +
geom_line(aes(linetype = storage)) +
geom_point(aes(shape = storage)) +
scale_y_log10(
breaks = scales::trans_breaks("log10", function(x) 10^x),
labels = scales::trans_format("log10", scales::math_format(10^x))
) +
theme_light() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")14.2.2 Daily downloads of CRAN packages
The CRAN downloads chart was generated through:
downloads_csv <- "data/01-intro-r-cran-downloads.csv"
if (!file.exists(downloads_csv)) {
downloads <- cranlogs::cran_downloads(from = "2014-01-01", to = "2019-01-01")
readr::write_csv(downloads, downloads_csv)
}
cran_downloads <- readr::read_csv(downloads_csv)
ggplot(cran_downloads, aes(date, count)) +
labs(title = "CRAN Packages",
subtitle = "Total daily downloads over time") +
geom_point(colour="black", pch = 21, size = 1) +
scale_x_date() + xlab("year") + ylab("downloads") +
scale_x_date(date_breaks = "1 year",
labels = function(x) substring(x, 1, 4)) +
scale_y_continuous(
limits = c(0, 3.5 * 10^6),
breaks = c(0.5 * 10^6, 10^6, 1.5 * 10^6, 2 * 10^6, 2.5 * 10^6, 3 * 10^6, 3.5 * 10^6),
labels = c("", "1M", "", "2M", "", "3M", "")
)14.3 Getting Started
14.3.1 Prerequisites
14.3.1.1 Installing R
From r-project.org, download and launch the R installer for your platform, Windows, Macs or Linux available.
FIGURE 14.1: The R Project for Statistical Computing
14.3.1.2 Installing Java
From java.com/download, download and launch the installer for your platform, Windows, Macs or Linux are also available.
FIGURE 14.2: Java Download Page
Starting with Spark 2.1, Java 8 is required; however, previous versions of Spark support Java 7. Regardless, we recommend installing Java Runtime Engine 8, or JRE 8 for short.
Note: For advanced readers that are already using the Java Development Kit, JDK for short. Please notice that JDK 9+ is currently unsupported so you will need to downgrade to JDK 8 by uninstalling JDK 9+ or by setting JAVA_HOME appropiately.
14.3.1.3 Installing RStudio
While installing RStudio is not strictly required to work with Spark with R, it will make you much more productive and therefore, I would recommend you take the time to install RStudio from rstudio.com/download, then download and launch the installer for your platform: Windows, Macs or Linux.
FIGURE 14.3: RStudio Downloads Page
After launching RStudio, you can use RStudio’s console panel to execute the code provided in this chapter.
14.3.1.4 Using RStudio
If you are not familiar with RStudio, you should make note of the following panes:
- Console: A standalone R console you can use to execute all the code presented in this book.
- Packages: This pane allows you to install
sparklyrwith ease, check its version, navigate to the help contents, etc. - Connections: This pane allows you to connecto to Spark, manage your active connection and view the available datasets.
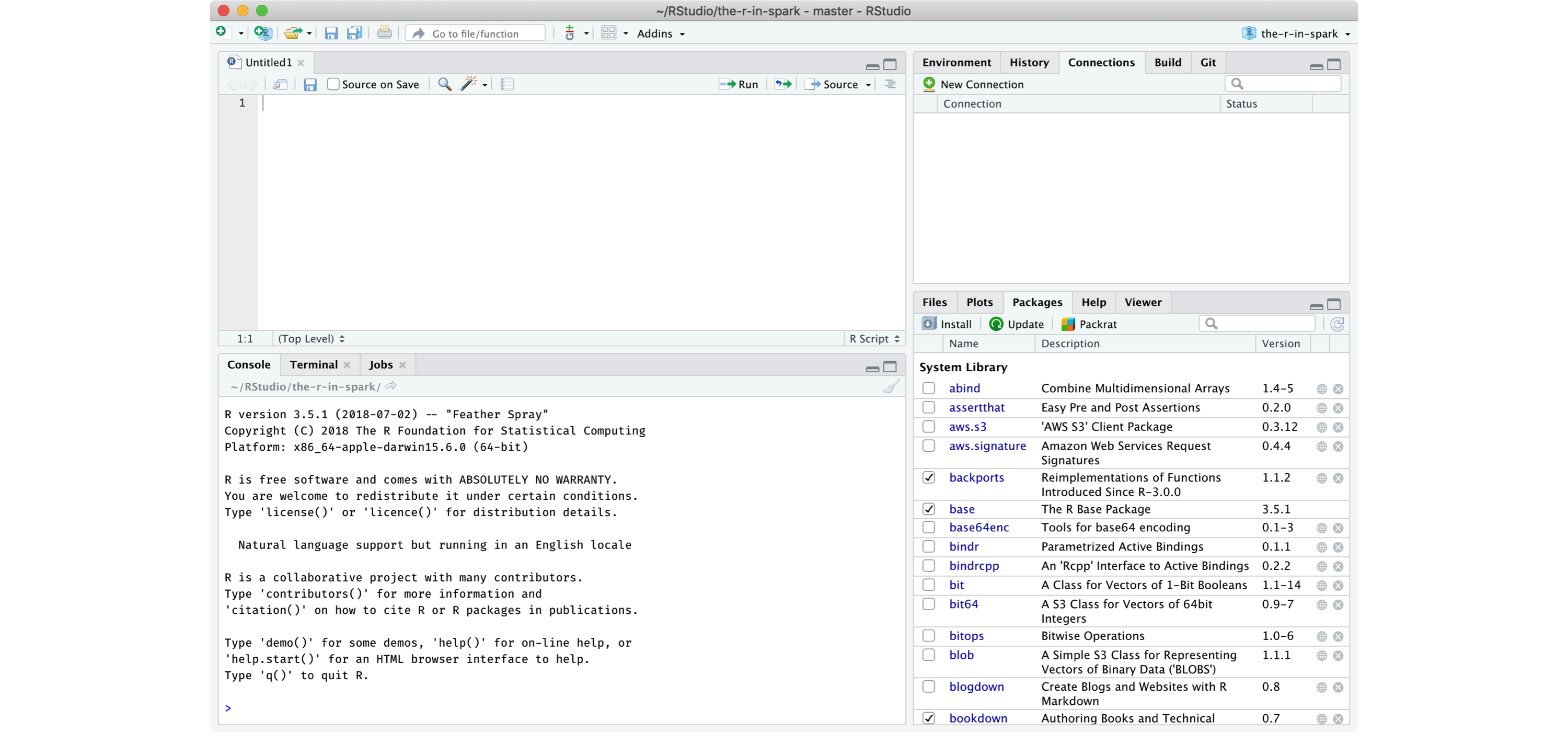
FIGURE 14.4: RStudio Overview
14.4 Analysis
14.4.1 Hive Functions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| size(Map<K.V>) | Returns the number of elements in the map type. |
| size(Array |
Returns the number of elements in the array type. |
| map_keys(Map<K.V>) | Returns an unordered array containing the keys of the input map. |
| map_values(Map<K.V>) | Returns an unordered array containing the values of the input map. |
| array_contains(Array |
Returns TRUE if the array contains value. |
| sort_array(Array |
Sorts the input array in ascending order according to the natural ordering of the array elements and returns it |
| binary(string or binary) | Casts the parameter into a binary. |
| cast(expr as ‘type’) | Converts the results of the expression expr to the given type. |
| from_unixtime(bigint unixtime[, string format]) | Converts the number of seconds from unix epoch (1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC) to a string. |
| unix_timestamp() | Gets current Unix timestamp in seconds. |
| unix_timestamp(string date) | Converts time string in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss to Unix timestamp (in seconds). |
| to_date(string timestamp) | Returns the date part of a timestamp string. |
| year(string date) | Returns the year part of a date. |
| quarter(date/timestamp/string) | Returns the quarter of the year for a date. |
| month(string date) | Returns the month part of a date or a timestamp string. |
| day(string date) dayofmonth(date) | Returns the day part of a date or a timestamp string. |
| hour(string date) | Returns the hour of the timestamp. |
| minute(string date) | Returns the minute of the timestamp. |
| second(string date) | Returns the second of the timestamp. |
| weekofyear(string date) | Returns the week number of a timestamp string. |
| extract(field FROM source) | Retrieve fields such as days or hours from source. Source must be a date, timestamp, interval or a string that can be converted into either a date or timestamp. |
| datediff(string enddate, string startdate) | Returns the number of days from startdate to enddate. |
| date_add(date/timestamp/string startdate, tinyint/smallint/int days) | Adds a number of days to startdate. |
| date_sub(date/timestamp/string startdate, tinyint/smallint/int days) | Subtracts a number of days to startdate. |
| from_utc_timestamp({any primitive type} ts, string timezone) | Converts a timestamp in UTC to a given timezone. |
| to_utc_timestamp({any primitive type} ts, string timezone) | Converts a timestamp in a given timezone to UTC. |
| current_date | Returns the current date. |
| current_timestamp | Returns the current timestamp. |
| add_months(string start_date, int num_months, output_date_format) | Returns the date that is num_months after start_date. |
| last_day(string date) | Returns the last day of the month which the date belongs to. |
| next_day(string start_date, string day_of_week) | Returns the first date which is later than start_date and named as day_of_week. |
| trunc(string date, string format) | Returns date truncated to the unit specified by the format. |
| months_between(date1, date2) | Returns number of months between dates date1 and date2. |
| date_format(date/timestamp/string ts, string fmt) | Converts a date/timestamp/string to a value of string in the format specified by the date format fmt. |
| if(boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull) | Returns valueTrue when testCondition is true, returns valueFalseOrNull otherwise. |
| isnull( a ) | Returns true if a is NULL and false otherwise. |
| isnotnull ( a ) | Returns true if a is not NULL and false otherwise. |
| nvl(T value, T default_value) | Returns default value if value is null else returns value. |
| COALESCE(T v1, T v2, …) | Returns the first v that is not NULL, or NULL if all v’s are NULL. |
| CASE a WHEN b THEN c [WHEN d THEN e]* [ELSE f] END | When a = b, returns c; when a = d, returns e; else returns f. |
| nullif( a, b ) | Returns NULL if a=b; otherwise returns a. |
| assert_true(boolean condition) | Throw an exception if ‘condition’ is not true, otherwise return null. |
| ascii(string str) | Returns the numeric value of the first character of str. |
| base64(binary bin) | Converts the argument from binary to a base 64 string. |
| character_length(string str) | Returns the number of UTF-8 characters contained in str. |
| chr(bigint | double A) |
| concat(string | binary A, string |
| context_ngrams(array<array |
Returns the top-k contextual N-grams from a set of tokenized sentences. |
| concat_ws(string SEP, string A, string B…) | Like concat() above, but with custom separator SEP. |
| decode(binary bin, string charset) | Decodes the first argument into a String using the provided character set (one of ‘US-ASCII’, ‘ISO-8859-1’, ‘UTF-8’, ‘UTF-16BE’, ‘UTF-16LE’, ‘UTF-16’). If either argument is null, the result will also be null. |
| elt(N int,str1 string,str2 string,str3 string,…) | Return string at index number, elt(2,‘hello’,‘world’) returns ‘world’. |
| encode(string src, string charset) | Encodes the first argument into a BINARY using the provided character set (one of ‘US-ASCII’, ‘ISO-8859-1’, ‘UTF-8’, ‘UTF-16BE’, ‘UTF-16LE’, ‘UTF-16’). |
| field(val T,val1 T,val2 T,val3 T,…) | Returns the index of val in the val1,val2,val3,… list or 0 if not found. |
| find_in_set(string str, string strList) | Returns the first occurance of str in strList where strList is a comma-delimited string. |
| format_number(number x, int d) | Formats the number X to a format like '#,###,###.##', rounded to D decimal places, and returns the result as a string. If D is 0, the result has no decimal point or fractional part. |
| get_json_object(string json_string, string path) | Extracts json object from a json string based on json path specified, and returns json string of the extracted json object. |
| in_file(string str, string filename) | Returns true if the string str appears as an entire line in filename. |
| instr(string str, string substr) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of substr in str. |
| length(string A) | Returns the length of the string. |
| locate(string substr, string str[, int pos]) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of substr in str after position pos. |
| lower(string A) lcase(string A) | Returns the string resulting from converting all characters of B to lower case. |
| lpad(string str, int len, string pad) | Returns str, left-padded with pad to a length of len. If str is longer than len, the return value is shortened to len characters. |
| ltrim(string A) | Returns the string resulting from trimming spaces from the beginning(left hand side) of A. |
| ngrams(array<array |
Returns the top-k N-grams from a set of tokenized sentences, such as those returned by the sentences() UDAF. |
| octet_length(string str) | Returns the number of octets required to hold the string str in UTF-8 encoding. |
| parse_url(string urlString, string partToExtract [, string keyToExtract]) | Returns the specified part from the URL. Valid values for partToExtract include HOST, PATH, QUERY, REF, PROTOCOL, AUTHORITY, FILE, and USERINFO. |
| printf(String format, Obj… args) | Returns the input formatted according do printf-style format strings. |
| regexp_extract(string subject, string pattern, int index) | Returns the string extracted using the pattern. |
| regexp_replace(string INITIAL_STRING, string PATTERN, string REPLACEMENT) | Returns the string resulting from replacing all substrings in INITIAL_STRING that match the java regular expression syntax defined in PATTERN with instances of REPLACEMENT. |
| repeat(string str, int n) | Repeats str n times. |
| replace(string A, string OLD, string NEW) | Returns the string A with all non-overlapping occurrences of OLD replaced with NEW. |
| reverse(string A) | Returns the reversed string. |
| rpad(string str, int len, string pad) | Returns str, right-padded with pad to a length of len. |
| rtrim(string A) | Returns the string resulting from trimming spaces from the end(right hand side) of A. |
| sentences(string str, string lang, string locale) | Tokenizes a string of natural language text into words and sentences, where each sentence is broken at the appropriate sentence boundary and returned as an array of words. |
| space(int n) | Returns a string of n spaces. |
| split(string str, string pat) | Splits str around pat (pat is a regular expression). |
| str_to_map(text[, delimiter1, delimiter2]) | Splits text into key-value pairs using two delimiters. Delimiter1 separates text into K-V pairs, and Delimiter2 splits each K-V pair. Default delimiters are ‘,’ for delimiter1 and ‘:’ for delimiter2. |
| substr(string | binary A, int start) |
| substring_index(string A, string delim, int count) | Returns the substring from string A before count occurrences of the delimiter delim. |
| translate(string | char |
| trim(string A) | Returns the string resulting from trimming spaces from both ends of A. |
| unbase64(string str) | Converts the argument from a base 64 string to BINARY. |
| upper(string A) ucase(string A) | Returns the string resulting from converting all characters of A to upper case. For example, upper(‘fOoBaR’) results in ‘FOOBAR’. |
| initcap(string A) | Returns string, with the first letter of each word in uppercase, all other letters in lowercase. Words are delimited by whitespace. |
| levenshtein(string A, string B) | Returns the Levenshtein distance between two strings. |
| soundex(string A) | Returns soundex code of the string. |
| mask(string str[, string upper[, string lower[, string number]]]) | Returns a masked version of str. |
| mask_first_n(string str[, int n]) | Returns a masked version of str with the first n values masked. mask_first_n(“1234-5678-8765-4321”, 4) results in nnnn-5678-8765-4321. |
| mask_last_n(string str[, int n]) | Returns a masked version of str with the last n values masked. |
| mask_show_first_n(string str[, int n]) | Returns a masked version of str, showing the first n characters unmasked. |
| mask_show_last_n(string str[, int n]) | Returns a masked version of str, showing the last n characters unmasked. |
| mask_hash(string | char |
| java_method(class, method[, arg1[, arg2..]]) | Synonym for reflect. |
| reflect(class, method[, arg1[, arg2..]]) | Calls a Java method by matching the argument signature, using reflection. |
| hash(a1[, a2…]) | Returns a hash value of the arguments. |
| current_user() | Returns current user name from the configured authenticator manager. |
| logged_in_user() | Returns current user name from the session state. |
| current_database() | Returns current database name. |
| md5(string/binary) | Calculates an MD5 128-bit checksum for the string or binary. |
| sha1(string/binary)sha(string/binary) | Calculates the SHA-1 digest for string or binary and returns the value as a hex string. |
| crc32(string/binary) | Computes a cyclic redundancy check value for string or binary argument and returns bigint value. |
| sha2(string/binary, int) | Calculates the SHA-2 family of hash functions (SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512). |
| aes_encrypt(input string/binary, key string/binary) | Encrypt input using AES. |
| aes_decrypt(input binary, key string/binary) | Decrypt input using AES. |
| version() | Returns the Hive version. |
| count(expr) | Returns the total number of retrieved rows. |
| sum(col), sum(DISTINCT col) | Returns the sum of the elements in the group or the sum of the distinct values of the column in the group. |
| avg(col), avg(DISTINCT col) | Returns the average of the elements in the group or the average of the distinct values of the column in the group. |
| min(col) | Returns the minimum of the column in the group. |
| max(col) | Returns the maximum value of the column in the group. |
| variance(col), var_pop(col) | Returns the variance of a numeric column in the group. |
| var_samp(col) | Returns the unbiased sample variance of a numeric column in the group. |
| stddev_pop(col) | Returns the standard deviation of a numeric column in the group. |
| stddev_samp(col) | Returns the unbiased sample standard deviation of a numeric column in the group. |
| covar_pop(col1, col2) | Returns the population covariance of a pair of numeric columns in the group. |
| covar_samp(col1, col2) | Returns the sample covariance of a pair of a numeric columns in the group. |
| corr(col1, col2) | Returns the Pearson coefficient of correlation of a pair of a numeric columns in the group. |
| percentile(BIGINT col, p) | Returns the exact pth percentile of a column in the group (does not work with floating point types). p must be between 0 and 1. |
| percentile(BIGINT col, array(p1 [, p2]…)) | Returns the exact percentiles p1, p2, … of a column in the group. pi must be between 0 and 1. |
| percentile_approx(DOUBLE col, p [, B]) | Returns an approximate pth percentile of a numeric column (including floating point types) in the group. The B parameter controls approximation accuracy at the cost of memory. Higher values yield better approximations, and the default is 10,000. When the number of distinct values in col is smaller than B, this gives an exact percentile value. |
| percentile_approx(DOUBLE col, array(p1 [, p2]…) [, B]) | Same as above, but accepts and returns an array of percentile values instead of a single one. |
| regr_avgx(independent, dependent) | Equivalent to avg(dependent). |
| regr_avgy(independent, dependent) | Equivalent to avg(independent). |
| regr_count(independent, dependent) | Returns the number of non-null pairs used to fit the linear regression line. |
| regr_intercept(independent, dependent) | Returns the y-intercept of the linear regression line, i.e. the value of b in the equation dependent = a * independent + b. |
| regr_r2(independent, dependent) | Returns the coefficient of determination for the regression. |
| regr_slope(independent, dependent) | Returns the slope of the linear regression line, i.e. the value of a in the equation dependent = a * independent + b. |
| regr_sxx(independent, dependent) | Equivalent to regr_count(independent, dependent) * var_pop(dependent). |
| regr_sxy(independent, dependent) | Equivalent to regr_count(independent, dependent) * covar_pop(independent, dependent). |
| regr_syy(independent, dependent) | Equivalent to regr_count(independent, dependent) * var_pop(independent). |
| histogram_numeric(col, b) | Computes a histogram of a numeric column in the group using b non-uniformly spaced bins. The output is an array of size b of double-valued (x,y) coordinates that represent the bin centers and heights |
| collect_set(col) | Returns a set of objects with duplicate elements eliminated. |
| collect_list(col) | Returns a list of objects with duplicates. |
| ntile(INTEGER x) | Divides an ordered partition into x groups called buckets and assigns a bucket number to each row in the partition. This allows easy calculation of tertiles, quartiles, deciles, percentiles and other common summary statistics. |
| explode(ARRAY |
Explodes an array to multiple rows. Returns a row-set with a single column (col), one row for each element from the array. |
| explode(MAP<Tkey,Tvalue> m) | Explodes a map to multiple rows. Returns a row-set with a two columns (key,value) , one row for each key-value pair from the input map. |
| posexplode(ARRAY |
Explodes an array to multiple rows with additional positional column of int type (position of items in the original array, starting with 0). Returns a row-set with two columns (pos,val), one row for each element from the array. |
| inline(ARRAY<STRUCT<f1:T1,…,fn:Tn>> a) | Explodes an array of structs to multiple rows. Returns a row-set with N columns (N = number of top level elements in the struct), one row per struct from the array. |
| stack(int r,T1 V1,…,Tn/r Vn) | Breaks up n values V1,…,Vn into r rows. Each row will have n/r columns. r must be constant. |
| json_tuple(string jsonStr,string k1,…,string kn) | Takes JSON string and a set of n keys, and returns a tuple of n values. |
| parse_url_tuple(string urlStr,string p1,…,string pn) | Takes URL string and a set of n URL parts, and returns a tuple of n values. |
14.5 Modeling
14.5.1 MLlib Functions
The following table exhibits the ML algorithms supported in sparklyr:
14.5.1.1 Classification
| Algorithm | Function |
|---|---|
| Decision Trees | ml_decision_tree_classifier() |
| Gradient-Boosted Trees | ml_gbt_classifier() |
| Linear Support Vector Machines | ml_linear_svc() |
| Logistic Regression | ml_logistic_regression() |
| Multilayer Perceptron | ml_multilayer_perceptron_classifier() |
| Naive-Bayes | ml_naive_bayes() |
| One vs Rest | ml_one_vs_rest() |
| Random Forests | ml_random_forest_classifier() |
14.5.1.2 Regression
| Algorithm | Function |
|---|---|
| Accelerated Failure Time Survival Regression | ml_aft_survival_regression() |
| Decision Trees | ml_decision_tree_regressor() |
| Generalized Linear Regression | ml_generalized_linear_regression() |
| Gradient-Boosted Trees | ml_gbt_regressor() |
| Isotonic Regression | ml_isotonic_regression() |
| Linear Regression | ml_linear_regression() |
14.5.1.3 Clustering
| Algorithm | Function |
|---|---|
| Bisecting K-Means Clustering | ml_bisecting_kmeans() |
| Gaussian Mixture Clustering | ml_gaussian_mixture() |
| K-Means Clustering | ml_kmeans() |
| Latent Dirichlet Allocation | ml_lda() |
14.5.1.4 Recommendation
| Algorithm | Function |
|---|---|
| Alternating Least Squares Factorization | ml_als() |
14.5.1.5 Frequent Pattern Mining
| Algorithm | Function |
|---|---|
| FPGrowth | ml_fpgrowth() |
14.5.1.6 Feature Transformers
| Transformer | Function |
|---|---|
| Binarizer | ft_binarizer() |
| Bucketizer | ft_bucketizer() |
| Chi-Squared Feature Selector | ft_chisq_selector() |
| Vocabulary from Document Collections | ft_count_vectorizer() |
| Discrete Cosine Transform | ft_discrete_cosine_transform() |
| Transformation using dplyr | ft_dplyr_transformer() |
| Hadamard Product | ft_elementwise_product() |
| Feature Hasher | ft_feature_hasher() |
| Term Frequencies using Hashing | export(ft_hashing_tf) |
| Inverse Document Frequency | ft_idf() |
| Imputation for Missing Values | export(ft_imputer) |
| Index to String | ft_index_to_string() |
| Feature Interaction Transform | ft_interaction() |
| Rescale to [-1, 1] Range | ft_max_abs_scaler() |
| Rescale to [min, max] Range | ft_min_max_scaler() |
| Locality Sensitive Hashing | ft_minhash_lsh() |
| Converts to n-grams | ft_ngram() |
| Normalize using the given P-Norm | ft_normalizer() |
| One-Hot Encoding | ft_one_hot_encoder() |
| Feature Expansion in Polynomial Space | ft_polynomial_expansion() |
| Maps to Binned Categorical Features | ft_quantile_discretizer() |
| SQL Transformation | ft_sql_transformer() |
| Standardizes Features using Corrected STD | ft_standard_scaler() |
| Filters out Stop Words | ft_stop_words_remover() |
| Map to Label Indices | ft_string_indexer() |
| Splits by White Spaces | ft_tokenizer() |
| Combine Vectors to Row Vector | ft_vector_assembler() |
| Indexing Categorical Feature | ft_vector_indexer() |
| Subarray of the Original Feature | ft_vector_slicer() |
| Transform Word into Code | ft_word2vec() |
14.6 Clusters
14.6.1 Google trends for mainframes, cloud computing and kubernetes
Data downloaded from https://bit.ly/2YnHkNI.
library(dplyr)
read.csv("data/clusters-trends.csv", skip = 2) %>%
mutate(year = as.Date(paste(Month, "-01", sep = ""))) %>%
mutate(`On-Premise` = `mainframe...Worldwide.`,
Cloud = `cloud.computing...Worldwide.`,
Kubernetes = `kubernetes...Worldwide.`) %>%
tidyr::gather(`On-Premise`, Cloud, Kubernetes,
key = "trend", value = "popularity") %>%
ggplot(aes(x=year, y=popularity, group=trend)) +
geom_line(aes(linetype = trend, color = trend)) +
scale_x_date(date_breaks = "2 year", date_labels = "%Y") +
labs(title = "Cluster Computing Trends",
subtitle = paste("Search popularity for on-premise (mainframe)",
"cloud computing and kubernetes ")) +
scale_color_grey(start = 0.6, end = 0.2) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0, size = 1, colour = "#333333") +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank())14.7 Streaming
14.7.1 Stream Generator
The stream_generate_test() function creates a local test stream. This function works independently from a Spark connection. The following example will create five files in sub-folder called “source”. The files will be created one second apart from the previous file’s creation.
After the function completes, all of the files should show up in the “source” folder. Notice that the file size vary. This is so that it simulates what a true stream would do.
## size
## source/stream_1.csv 44
## source/stream_2.csv 121
## source/stream_3.csv 540
## source/stream_4.csv 2370
## source/stream_5.csv 7236The stream_generate_test() by default will create a single numeric variable data frame.
## # A tibble: 1,489 x 1
## x
## <dbl>
## 1 630
## 2 631
## 3 632
## 4 633
## 5 634
## 6 635
## 7 636
## 8 637
## 9 638
## 10 639
## # ... with 1,479 more rows14.7.2 Installing Kafka
This instructions were put together using information from the official Kafka site. Specifically from the Quickstart page, and at the time of writing this book. Newer versions of Kafka undoubtely will be available when reading this book. The idea is to “timestamp” the versions used in the example in the Streaming chapter.
Download Kafka
wget http://apache.claz.org/kafka/2.2.0/kafka_2.12-2.2.0.tgzExpand the tar file and enter the new folder
tar -xzf kafka_2.12-2.2.0.tgz cd kafka_2.12-2.2.0Start the Zookeeper service that comes with Kafka
bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.propertiesStart the Kafka service
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
Make sure to always start Zookeper first, and then Kafka.